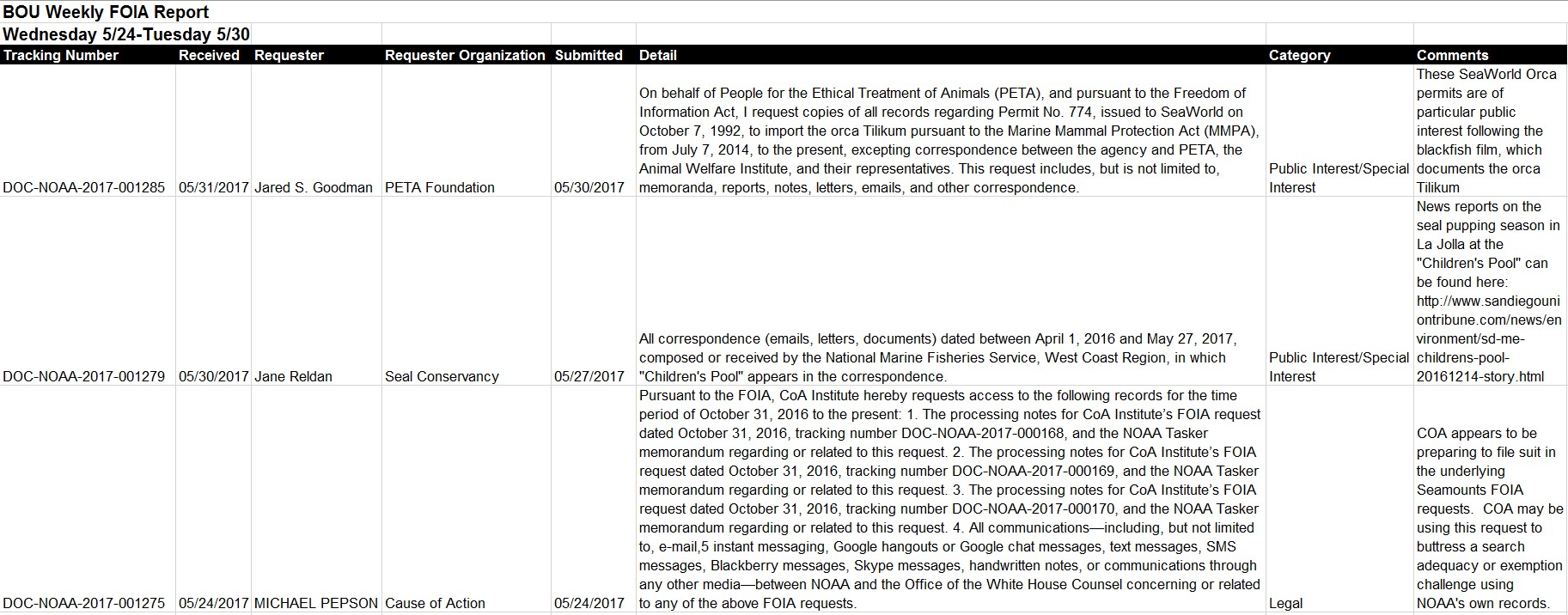
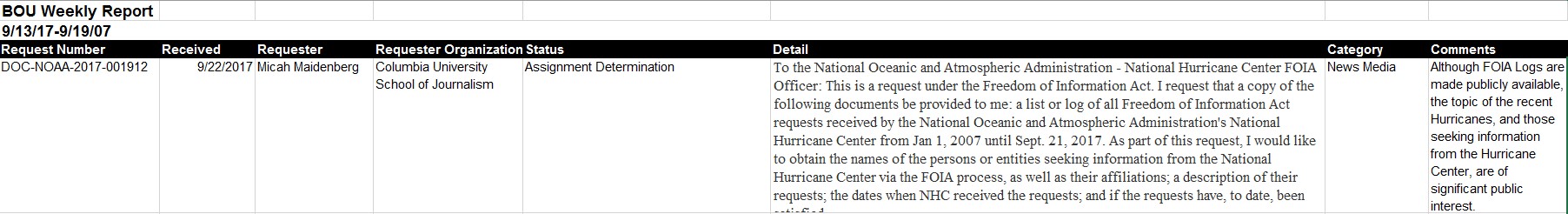
The Freedom of Information Act (“FOIA”) was introduced to ensure public access to records of the Executive Branch. Unfortunately, agency FOIA processes have long suffered from politicization at the hands of bureaucrats and political appointees who hope to frustrate the disclosure of embarrassing or newsworthy documents. A recent report about enhanced “vetting” of FOIA requests at the Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”), for example, demonstrates the tenacity of those who govern—regardless of their political affiliation—to keep secrets from the concerned public. Similarly, earlier this year, Cause of Action Institute (“CoA Institute”) revealed how the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration expanded its “sensitive review” procedures by putting records requests from attorneys, and requests concerning the Trump Administration’s transition period, into special processing categories. Now, newly disclosed records from the Federal Aviation Administration (“FAA”) demonstrate how that agency has made concerted efforts to keep tabs on news media requesters.
The FAA’s FOIA “Media Reports”
“Sensitive review” refers to the practice of giving certain FOIA requests extra scrutiny, usually because the records at issue are politically damaging, embarrassing, or otherwise newsworthy. Politicization can come in different forms. Sometimes sensitive review entails an agency’s public affairs team or communications specialists being kept informed of new requests or outgoing productions of records. In other instances, it involves political appointees supervising searches or making redaction decisions. In all cases, sensitive review delays, and sometimes prevents, the disclosure of records that the public has a right to view.
According to records obtained by former CoA Institute attorney Allan Blutstein, the FAA’s sensitive review process includes a “tracking system” for requests submitted by representatives of the news media. News media requesters automatically receive a fee reduction under the FOIA and presumptively satisfy some of the requirements for expedited processing. This preferential treatment is meant to recognize the vital role of the media in a participatory democracy. The intentional targeting of media requesters within a framework for sensitive review, therefore, is especially concerning.
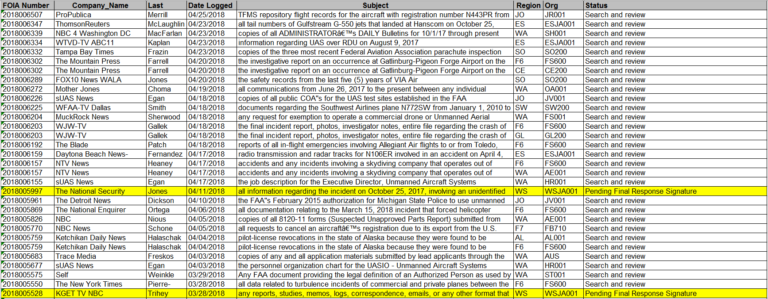
The following screenshot from one of the FAA’s “Media Request” charts shows just how the agency tracks pending requests. Each line includes a description of the records at issue and each request’s processing “status,” such as whether a search has been conducted or responsive records are under review.
Although approximately half of the requests recorded in the FAA chart (100 of 184) were submitted during the Trump Administration, the remainder date from as early as April 2009. Not only does this reveal an unacceptable backlog at the FAA, but it suggests that the practice of targeting media requesters for special scrutiny or “tracking” may have originated with the Obama White House. CoA Institute warned in early 2014 that FOIA processes across the government were being clogged up by political intervention because of news media requesters seeking the disclosure of records about embarrassing scandals. It appears that the FAA’s current practice reflects the politicization that was covertly emphasized by the Obama Administration.
(A complete copy of the FAA tracking chart is available here. FOIA requests highlighted in blue have not yet been assigned to a FOIA officer, while requests in yellow are, in most cases, pending legal, business or supervisor review. An agency-created summary of the highlighted FOIA cases is available here.)
As a representative of the news media, CoA Institute itself was subject to the FAA’s tracking regime. Three of our pending requests, dating from early 2012 and 2013, were flagged. One of those three requests has not even been assigned to a disclosure officer for processing, despite the fact that it was submitted to the FAA almost five years ago.
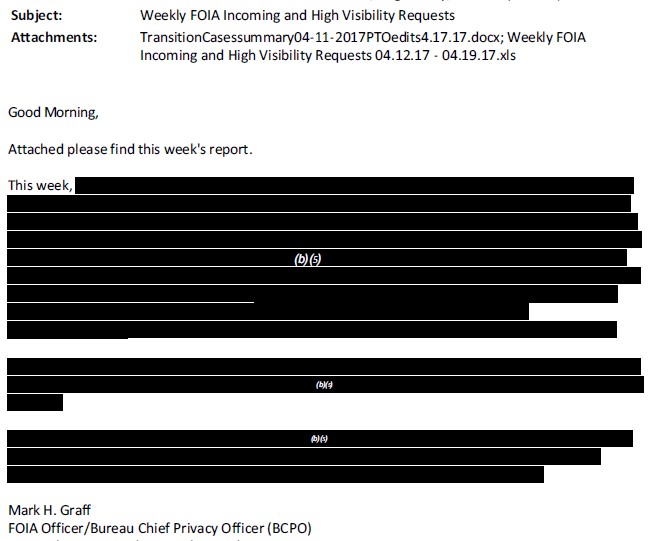
The version of the FAA’s “Media Request” tracking table obtained by CoA Institute, which is dated April 26, 2018, was circulated amongst several officials within the FAA’s Office of Communications (“AOC”) and the Department of Transportation’s Office of the Secretary (“OST”). The cover email also includes a batch of incoming record requests. All of this suggests that a key group at the FAA is responsible for managing the sensitive review process and keeping key officials within the Administration knowledgeable about ongoing FOIA affairs.
A complete copy of this email is available here. To the extent we have been able to identify the individuals involved, we believe they hold the following positions within the FAA’s FOIA Office, Office of Communications, or the Office of the Secretary of Transportation:
- Kimberly McCormick – FOIA Management Specialist
- Kathy Ray – Departmental FOIA Officer, Department of Transportation
- Laura Brown – Deputy Assistant Administrator for Public Affairs
- Gary Kolb – Chief of Staff, Communications Division
- Greg Martin – Assistant Administrator for Communications
- Elisabeth Smeda – Senior Advisor to the Acting Administrator
- Collen Donovan – Senior Advisor to the Deputy Administrator
- Carlos Alfaro – Director, Information and Technology
- Geraldine Gour – Manager, Administrative Services for the Aircraft Certification Service
- Duke Taylor – Manager, FOIA Program
- Louis Fuss – Senior FOIA Management Specialist
- Laurie Karnay – FOIA Management Specialist
- Susan McLean – FOIA Management Specialist
- Delphine Ndi – FOIA Analyst
A collection of the incoming FOIA requests attached to the email is available here. Those requests were submitted by various reporters from Mother Jones, ABC, NBC, Fox10 News of Mobile, various local newspapers, and ProPublica.
The Problem of FOIA Politicization
Unfortunately, there is nothing unlawful about an agency keeping separate “tracking” notes on FOIA requests submitted by members of the media. Nor is there anything unlawful in an agency keeping its communications officials, or even other parts of the Executive Branch, aware of incoming requests or outgoing records that could elicit media coverage or public inquiries. But the sort of intentional tracking and obvious backlog that has become standard procedure at the FAA is unacceptable and clearly violates the spirit of the FOIA. The fact that requests from the beginning of 2009 are still pending is inexcusable. The real danger of politicization at the FAA should be self-evident. When an agency is committed to treating media requesters in a special way, the tendency will always be to delay and obstruct disclosure, thus impairing FOIA rights and inhibiting the proper functioning of a critical media.
Ever since President Trump took office, the transparency community—including CoA Institute—has raised valid concerns about the White House’s coordinated effort to stifle transparency, both in the context of FOIA and with respect to congressional inquiries and oversight requests. This is an unfortunate development, and CoA Institute remains committed to fighting for open government. But insofar as the current Administration questions the value of President Obama’s legacy, it should commit itself to greater transparency. The Washington Post described the Obama Administration as one of the “most secretive,” “most elusive,” and “most punitive toward whistleblowers and leakers who want to bring light to wrongdoing they have observed from inside powerful institutions.” The Trump Administration should endeavor to do better. No one should fear the disinfecting power of sunlight, and the federal government is always in need of some cleaning.
Ryan P. Mulvey is Counsel at Cause of Action Institute