Earlier this month, Cause of Action Institute (“CoA Institute”) filed an administrative appeal of a final response by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (“NOAA”) to CoA Institute’s Freedom of Information Act (“FOIA”) request concerning NOAA’s efforts to expand industry funded at-sea monitoring—specifically, to the herring and mackerel fisheries—and to lay the foundation for industry funding across all of New England and the Mid-Atlantic. NOAA’s processing of the request suggests that the agency failed to search email accounts belonging to members of the fishery management councils even though they are subject to public disclosure. Based on the limited records that were disclosed, NOAA’s search appears improperly limited to its own employees.
The Industry-Funded Monitoring Omnibus Amendment
Over the past five years, the New England and Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Councils (“NEFMC” and “MAFMC,” respectively) have worked on a controversial omnibus amendment that would require more fisherman to pay for at-sea monitoring. Industry-funded monitoring has already been imposed on the groundfish fleet, despite a long-fought legal challenge, devastating economic consequences, and historically-depressed fishery performance. Industry funding in the herring and mackerel fisheries will cost fishermen between $710–$818 per day at sea. That is more than the average daily revenue of many fishermen and will render fishing unprofitable for countless small-scale family businesses.
CoA Institute submitted a written comment in response to the poorly-designed and ill-timed omnibus amendment. Although the MAFMC decided to table the project for at least a year, the New England Council elected to forge ahead with the herring fishery. According to a recent presentation by NOAA staff, the agency is now reviewing a draft proposed rule. The NEFMC’s official “timeline” indicates the rule will be published this month. A final rule is expected to follow in June 2018.
The December 7, 2017 FOIA Request and Appeal
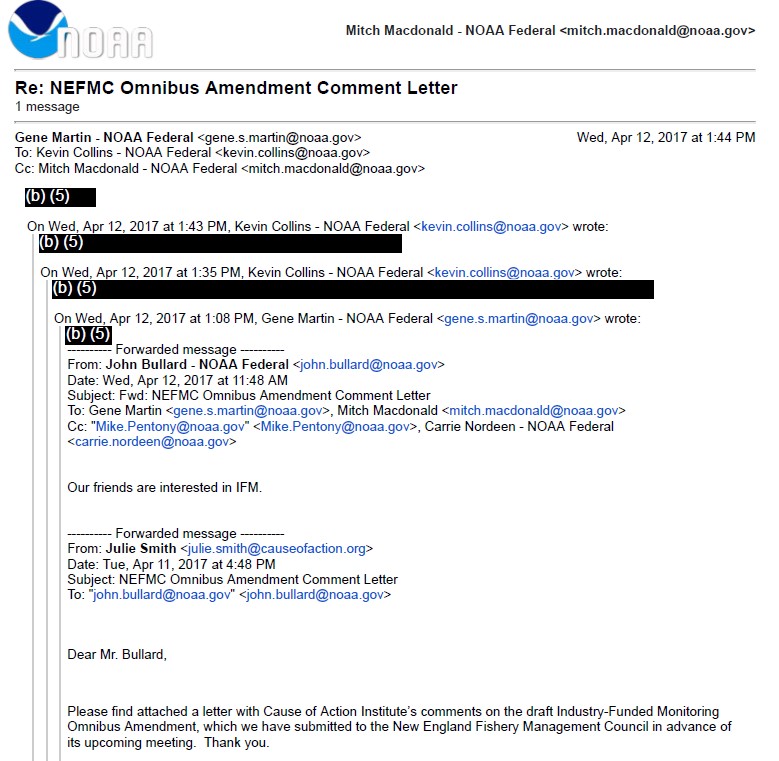
In an effort to investigate how the Councils and NOAA responded to our comment, we filed a FOIA request for “[a]ll records concerning” the comment, “including any correspondence between or amongst members of the New England and Mid-Atlantic Councils; officials, employees, or representatives of NOAA; or any other third party.” When we received a response, we were surprised that the agency only found seven responsive records—five of which were part of a single e-mail chain with most substantive content redacted to protect NOAA’s “deliberative” processes.
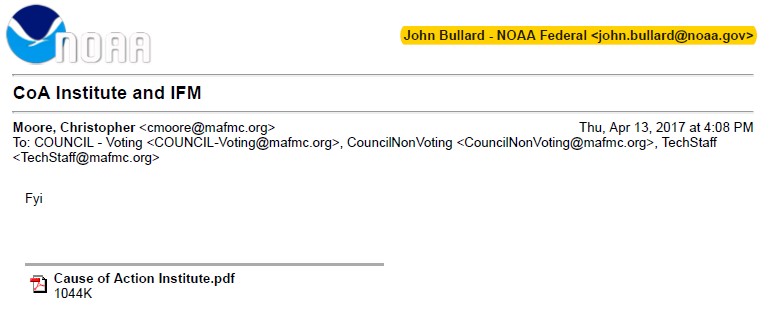
The other two records were an email that we sent to then-Regional Administrator John Bullard with a courtesy copy of our comment, and an email from Dr. Christopher Moore, Executive Director of the MAFMC, forwarding our comment to members of the Council.
NOAA failed to disclose any records from the members of the regional councils. Even the record from Dr. Moore was the version received by John Bullard, as highlighted here:
NOAA’s failure to locate, process, and disclose relevant records from Council members is a serious deficiency in its response. Council records—including members’ email correspondence—are subject to the FOIA, even if those records are stored in private email accounts. The regional councils conduct important business that has a serious impact on the livelihoods of Americans involved with the fishing industry. The process by which fishery rules are designed and implemented can already be less-than-transparent; any attempt to hide records from public scrutiny cannot be allowed to stand.
Follow-Up Public Records Requests to Massachusetts and Maryland
CoA Institute also filed state-level FOIA requests with Massachusetts and Maryland this week in order to access some of the records that NOAA has refused to disclose. These requests seek the same records sought from the federal government, but only to the extent they were created or received by John Quinn and Michael Luisi, the chairmen of the NEFMC and MAFMC, who used their state government email addresses to conduct council business.
Interestingly, sometime after CoA Institute submitted its comment, Dr. Quinn removed his University of Massachusetts email address from the NEFMC website, perhaps in order to dissuade the interested public from even attempting to file a state public records request.
CoA Institute is committed to fighting for the economic rights and liberties of everyday Americans, including those who face increasingly onerous regulation of their livelihoods. We also will fight against agencies that flout federal records management laws in an attempt to keep their regulatory efforts secret.
Ryan Mulvey is Counsel at Cause of Action Institute